Blog Categories

Learning Outcomes: Meaning, Examples & Objectives Difference
Today’s education is more than just memorising theories, lectures, and texts. Schools, universities, and even online courses now focus on what a student actually learns, not just what a teacher teaches. This shift has increased the importance of learning outcomes. It is a concept widely used in modern education, skill-based programmes, and professional training.
This blog explains what are learning outcomes, their examples, types, and how they differ from learning objectives, along with their importance in effective learning.
What are Learning Outcomes?
Learning outcomes are the information or abilities that students should have by the completion of a specific assignment, class, course, or programme. They help students:
- To recognise how such abilities and information will benefit them
- To emphasise the context and possible uses of knowledge and abilities
- To link education in a variety of settings
- By guiding them in directing review and assessment
Applying and integrating information is a key component of good learning outcomes. They describe how students will be able to use the material, both within and outside of the classroom, rather than concentrating on content covered.
Why are Learning Outcomes Important in Modern Education?
Learning outcomes play a key role in improving the quality of teaching and learning. Let’s explore how.
Benefits for Students
- Students are more engaged with their learning and the course material when they concentrate on applying the knowledge and skills they have learnt in the course and integrating them with other aspects of their lives.
- The focus on integration and transferable abilities increases student engagement by assisting students in making connections across courses and other types of information.
- Students are aware of the requirements and objectives of their evaluation.
Benefits for Teachers
- Creating these outcomes enables them to consider the course material and its possible uses, concentrating on the information and abilities that will be most useful to their students both now and in the future.
- They indicate effective assessment techniques.
- They give teachers the ability to establish the criteria by which the course’s effectiveness will be assessed.
Benefits for Institutions
- When a teacher evaluates a specific course or unit in light of upcoming assignments and the curriculum overall, it helps create a cohesive curriculum within a decentralised institution and guarantees that students are ready for work and learning in the future.
- They emphasise the application and integration of learning, which enhances student engagement, reveals opportunities for interdisciplinary study, and offers guidance and support to students with a wide range of prior academic preparation. These practices reflect and support the university’s contemporary nature and priorities.
- In addition to establishing frameworks for evaluating courses and programmes, they may help with curriculum and programme design, spot gaps or duplication in programme offerings, and define institutional, programmatic, and instructional priorities.
Also Read: Discover The Role Of Artificial Intelligence In Education
Difference Between Learning Outcomes and Objectives
Although often used together, learning objectives and outcomes are not the same. Let’s understand how.
| Comparison Point | Learning Objectives | Learning Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | What teachers will teach | What students will achieve |
| Measurability | Not always measurable | Always measurable |
| Orientation | Teacher-centred | Student-centred |
| Time | Before teaching begins | After course/lesson completion |
| Example | “The teacher will explain persuasive writing techniques.” | “Students will write a persuasive essay with correct formatting.” |
In simple words, ‘objective’ means ‘teaching goal’, and ‘outcome’ means ‘learning result’. Teachers plan objectives, but students demonstrate outcomes. This difference is important in professional education, where measurable results show whether teaching is effective.
Types of Learning Outcomes

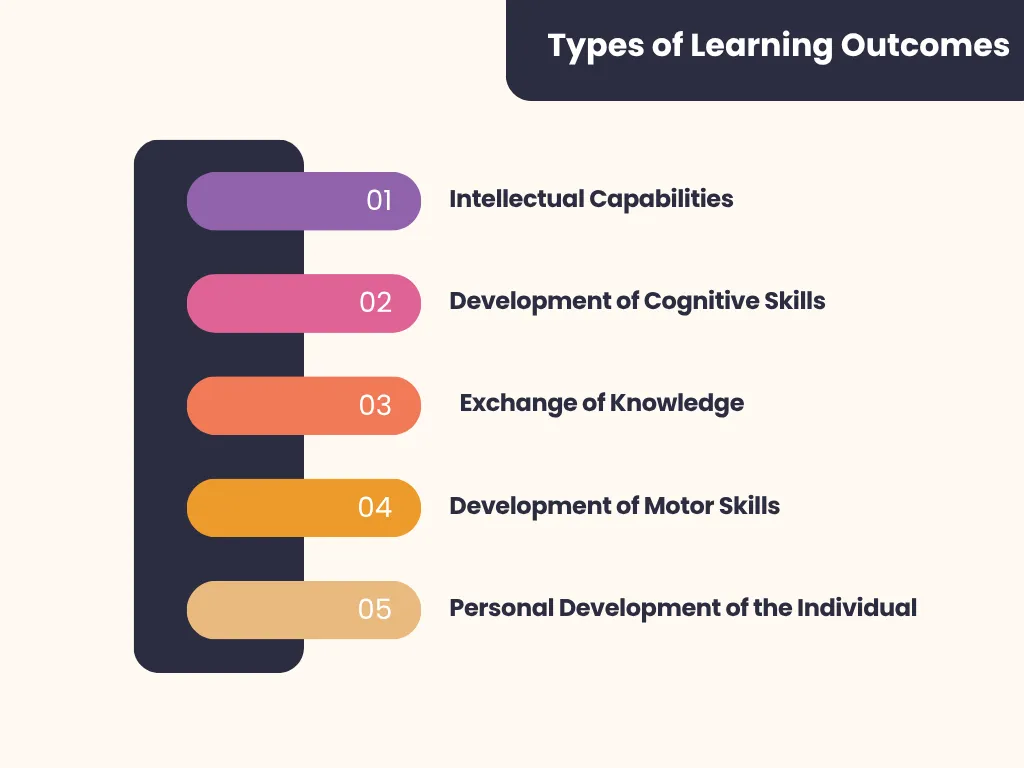
Given below are the different types of learning outcomes.
Intellectual Capabilities
To get the best learning results using this kind of learning outcome, students must be able to fully comprehend the subject. The fundamental learning result that is anticipated of a student is knowledge acquisition.
Development of Cognitive Skills
This learning objective pushes students to consider, evaluate, and fully comprehend the significance of a particular idea before acting appropriately.
Exchange of Knowledge
Students must be able to impart important knowledge to others. Students are therefore expected to develop a value system of knowledge by first acquiring it and then disseminating it to the world as part of this learning objective.
Development of Motor Skills
Enhancing a student’s capacity to plan and execute appropriate physical actions is the focus of motor skill development. They have to strive for their physical and general well-being.
Personal Development of the Individual
The internal state of the learner’s behaviour is reflected in this learning result. The ultimate level of learning is personal development in terms of knowledge, abilities, and capacity to produce something for society. The student must be able to manage their personal and professional lives and react appropriately to real-life situations.
The ultimate level of learning is personal development in terms of knowledge, abilities, and capacity to produce something for society. The student must be able to manage their personal and professional lives and react appropriately to real-life situations.
Learning Outcomes Examples
Let’s examine some actual examples of these outcomes from various tasks.
Task 1: A new hire onboarding course
Learning outcome: Students are able to recognise circumstances in which corporate policies are applicable and explain the appropriate course of action.
This outcome demonstrates that students comprehend and can remember new ideas, reflecting knowledge or intellectual abilities.
Task 2: A mediation seminar for HR officers
Learning outcome: Students can use dispute resolution techniques in actual work situations.
This outcome evaluates performance and shows if students are able to apply what they have learnt.
Task 3: A new product management software training session conducted online
Learning outcome: Students are able to use the programme and describe its features.
This result emphasises competency, demonstrating that students are capable of demonstrating a useful ability.
Task 4: A virtual reality training course on machine component replacement
Learning outcome: Students are able to insert and remove machine parts appropriately while providing an explanation of their actions.
This outcome emphasises a learner’s capacity to carry out activities physically and is related to motor skills.
Task 5: A talk about organisational tactics
Learning outcome: By describing concrete actions, students may show how they will apply organisational techniques.
This outcome deals with verbal knowledge and calls on students to express and apply what they have learnt.
These examples highlight that these learning outcomes make education practical, measurable, and skill-orientated.
How to Identify Positive Learning Outcomes
A well-written learning outcome focuses on what the student can demonstrate in a tangible way once they have finished the learning task. Only observable learning outcomes are beneficial. Therefore, it should incorporate the learner’s learning behaviours, the proper evaluation technique, and the particular success criteria.
Examples of strong learning outcomes:
- The ability of students to recognise the situations in which each of the five forms of conflict management should be used.
- Learners will be able to navigate and complete all training modules using the company’s LMS.
- Students will be able to analyse marketing data and make graphs with it.
- Students will be able to write SEO-optimised copy using the techniques recommended by the organisation.
- Students may appropriately develop case studies using industry requirements.
- The autoclaves can be cleaned and operated correctly by learners.
Examples of weak learning outcomes:
- Students will comprehend how to handle conflicts.
- Students will be familiar with the company’s LMS.
- Students will value the application of marketing data.
- Students will be aware of the business’s SEO strategies.
- Students will comprehend the components of a case study.
- Students will get knowledge about autoclaves.
To put it briefly, weak learning outcomes are ambiguous and challenging to evaluate, whereas strong ones are quantifiable and practical.
How to Create Learning Outcomes that Work for Every Learner
Whether you are in a classroom or a corporate environment, having explicit learning goals is crucial for effective training and education.
This is a methodical strategy for developing successful learning outcomes in many contexts, as mentioned below.
Determine the Learning Activity’s Goal
Make sure you understand the goal of the training session or class before determining results. The goal lays the groundwork for quantifiable results, whether it be skill development, compliance training, or the introduction of new ideas.
Describe What Success Means to Students
When creating a learning objective, consider what proficient students will be able to accomplish at the conclusion of the course or training. Consider observable behaviours. Will students be able to recognise, clarify, illustrate, or apply an idea, for instance?
Think About Several Forms of Education
Learning is more than just learning information by heart. Depending on the training or educational setting, learners may need to acquire physical skills, cognitive techniques, or intellectual abilities.
Make Sure the Results are Quantifiable
Effective results must be measurable via testing or observation. Can students successfully show their knowledge, do an assignment, or use a skill?
Align Results with Practical Uses
According to research, performance-based assessments—in which students use their knowledge or abilities in practical situations—are frequently more successful than standard knowledge examinations in gauging employee learning results.
Make results applicable by relating them to real-world applications. This guarantees that learning is useful outside of the classroom or training session and boosts engagement.
How Learning Outcomes Improve Effective Learning
Effective learning means students understand concepts deeply and can apply them—not just memorise. These outcomes directly support this by:
- Giving clear learning expectations
- Connecting teaching to real-life skills
- Making assessment more meaningful
- Helping students stay focused and motivated
- Allowing teachers to design better teaching strategies
For example, if a learning outcome says, “Students will create a multimedia presentation on climate change.”
It requires research, creativity, critical thinking, and communication—all key elements of effective learning.
Course Outcomes and Their Role
At the university level, every subject or course has a defined Course Outcome(s) (COs).
A course outcome explains what a student will achieve after completing the entire subject or semester.
Example of COs:
- Apply programming logic to solve real problems
- Understand marketing principles and apply them to case studies
- Conduct laboratory experiments and analyse results
Course outcomes ensure learning is job-orientated, practical, and aligned with industry requirements.
Teaching Objective
Teaching objectives guide teachers in planning lessons. They explain what a teacher intends to cover:
- Explain the chapter
- Introduce new concepts
- Conduct activities
- Provide notes and assignments
But the outcome shows whether these efforts worked. Teaching objectives lead to learning objectives, which in turn lead to learning outcomes.
Role of K.R. Mangalam University (KRMU) in Outcome-Based Education
Below are the points that show how K.R. Mangalam University ensures strong learning outcomes. The university offers:
- Industry-focused curriculum
- Practical training, labs, simulations, internships
- Project-based learning and real-world exposure
- Continuous assessment to check learning progress
- Faculty mentoring and skill development sessions
As a result, students don’t just learn theory, but they also gain practical knowledge, employability skills, communication abilities, and confidence for career success.
Conclusion
We have understood how and why learning outcomes are an essential part of modern education. They provide clarity, direction, and measurable achievements for both teachers and students. Whether in schools, universities, or corporate training, they ensure that knowledge turns into skills and learning leads to real progress. Students become more confident and goal-orientated, teachers plan better lessons and employers get industry-ready professionals.
With outcome-based learning, education becomes meaningful, skill-driven, and future-focused—and this is exactly what institutes like KRMU aim to deliver.
Also Read: What Is The Importance Of Inclusive Education
FAQs
Q1. What are learning outcomes?
Learning outcomes are measurable statements describing what a student will know or be able to do after completing a course or lesson.
Q2. What is the difference between learning outcomes and objectives?
Learning objectives are teaching goals, while learning outcomes are measurable results of what students actually learn.
Q3. Where are learning outcomes used?
Learning outcomes are used in schools, colleges, skill training programmes, online courses, and corporate training.
Q4. Why are learning outcomes important?
They improve teaching quality, student performance, and assessment.
Recent Post
All India Forensic Science Entrance Test (AIFSET-2026) Details and Eligibility
Explore the Top Artificial Intelligence University in India
BBA HR Management Syllabus: Semester-Wise Detailed Curriculum
Best AI Colleges in India 2025: Rankings, Fees, Admissions & Placement Insights
Best Universities in Delhi NCR 2025: Rankings, Admissions & Fees Guide
Top Engineering Colleges in Gurgaon 2025-26: Admission, Fees & Placement Guide
Explore the Best Courses After Graduation for High Salary
BSc Data Science: Syllabus, Careers, and Data Science Course
Understanding the Difference Between Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Is Data Science a Good Career Choice? Salary, Scope & Future Growth Explained
Integrated Course After 12th: Complete Guide, List and Benefits
Moot Court for Law Students: Its Importance and Objectives
CAT 2025: Exam Date, Eligibility, Syllabus, Registration & Preparation Tips
Explore the Best College for MBA in Marketing in Delhi NCR
Career Guidance and Counselling: Expert Support for a Successful Future
Importance of Internships: Boost Your Career with Real-World Experience
CUET Result 2025 Out: Check Scores, Cut-Offs & What to Do Next
Pursue Bachelor’s Degree in Journalism & Mass Communication at KRMU
BCA Course After 12th: Best College, Fees, Curriculum and More
BBA in Digital Marketing: Eligibility, Subjects, Fee and Scope
Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering: Eligibility, Admission and Fee Details
B Pharmacy Admission 2025: Course Details | Eligibility | Career
Is B.Sc. Computer Science Worth It? Salary, Scope & Future Prospects
KRMU: The Destination to Become a Future-Ready Software Engineer
Ph.D. Pharmaceutical Sciences: Course Details and Admission Process
Why KRMU is the Best College for BCom Hons. in Gurugram, Delhi NCR
JEE Mains 2025 Exam Date: Syllabus, Last date, Registration Date
Career After MA English: High Paying Jobs and Government Roles
B.Sc. Full Form Explained: Courses, Eligibility, Jobs & Admission
Why K.R. Mangalam University Is The Best Fine Arts University in India
Benefits of a Culinary Arts Bachelor Degree for Aspiring Chefs
Architecture Careers In India: Your Path To A Successful Future
Is NTA CUET UG Score Mandatory For Admission In All Universities
Choosing The Best B Sc Courses After 12th: A Detailed Guide To Your Future
Data Science and Artificial Intelligence: Revolutionising the Digital Age
Exploring Top Career Options For Commerce Students After The 12th
Exploring The Best Course After B Com To Elevate Future Prospects
The Difference between BE and BTech: Everything you need to know
Exploring Jobs After BSc Chemistry: Private And Government Jobs
What Are Some of The Best Professional Courses After 12th Class
Architecture Courses after 12th: Duration, Eligibility, Career Options
Why KRMU Is Considered One Of The Best BSc Agriculture Colleges In India?
A Complete Guide On Full Stack Development: Career Paths/Eligibility/Duration
Why KRMU Is Considered One Of The Best Hotel Management Colleges In India
Hotel Management Course Fees in Private College: What You Need to Know
Everything You Need to Know About Integrating Dual Degree Programs
Textile Design Course, Eligibility and Career Opportunities
Physiotherapy Course Fees: Career Paths/Eligibility Criteria/Top Colleges
Exploring BJMC Colleges in Delhi: Your Comprehensive Guide
A Comprehensive Guide B Pharm Duration, Syllabus, Job Opportunities
BCA Full Form And Subjects- Comprehensive Understanding Of BCA
Complete Guide of B Sc Agriculture Course Duration, Admission Process, Fees
A Detailed Guide On How To Become A Fashion Designer After 12th
Navigating Sustainability Trends: Preparing Students for Corporate Priorities in 2024
What Can I Do After a BA? Exploring Career Options for Bachelor of Arts Graduates
List Of Top Career Options After B.Tech Computer Science & Engineering
How to Choose the Right 12th Commerce Courses for Your Salary?
K.R. Mangalam University: A Leading University For Comprehensive Excellence
Understanding BBA Travel & Tourism: A Gateway To A Thriving Future
A Journey through K.R. Mangalam University’s as a Student of B.A. Honours Psychology
Why Choose B Tech Cyber Security: Learn Eligibility/Benefits/Career/College
List of B.Tech Courses: Various Specialisations/Eligibility Criteria/Careers
Benefits of Pursuing An MBA After BA: Career/Specialisations/Entrance Exam
Essential Guide On KR Mangalam University Scholarship For 2024-25
Everything You Need To Know About Architecture And Design in 2024
Exploring the UX/UI Race in B.Tech. Computer Science & Engineering
Exploring the UX/UI Race in B.Tech. Computer Science & Engineering
The Rising Demand For Management Professionals In The Country
B.Tech Computer Science Course: Eligibility, Syllabus, Exams, Fees, Scope
Exploring a BBA in Finance: Your Comprehensive Guide to a Promising Career Path
Compelling Reasons to Choose a BBA Program in Travel and Tourism
BA Political Science Honours: Your Path to Political Insight
Beyond Fashion Designing: Exploring the Creative World of B.A. Arts
Unlocking the Path to Success: Your Thriving Career in Cyber Security
Soaring to New Heights: Apeejay Professor Takes Flight as Certified Drone Flyer
D Pharmacy Course Details: Eligibility, Admissions & Subjects
The Art of Public Speaking: Tips for Confident Presentations
Advancing Your Career: Pursuing Diploma Courses After 10th Grade
Computer Science Engineering: Unraveling the Realm of Technology and Innovation
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Data Science Course for Your Career
Internship and Practical Training Opportunities for B.Com (Honours) Students
Exploring Career Scope of Pharmacology: A Promising Pathway
The Rise of Fintech: Revolutionizing India’s Financial Landscape
The Advancement Postgraduate Courses in India Career Development
Mastering Time Management: A Key to Success in Work and Life
Understanding the Difference Between Psychologist and Psychiatrist
Career in Fashion Designing: Full Guide from Start to Destination
Diploma Course vs Degree Course: Exploring the Pros and Cons
Must Watch Movies and Web series For Forensic Science Student
Exploring a Career in Criminal Law: An In-Depth Guide to LLB Criminal Law
Unveiling the Role of a Supply Chain Analyst: A Path to Success
Comparing CSE and IT: Unveiling Distinctions and Career Opportunities
Exploring the Educational Landscape: Top Universities in Gurgaon
Architecture Course: Guide to Becoming an Architect in India
Traditional Marketing vs Digital Marketing: Exploring their Pros and Cons
The Basics of B Tech: What You Need to Know to Pursue a Degree in Technology
Is Pursuing MBA After Engineering an Excellent Career Choice
How To Become An Interior Designer in India: Qualification & Career Scopes
Exploring the Benefits of an International Accounting and Finance Course
BA LLB (Hons): A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Program
5 Full Stack Web Development Course Lessons from the Professionals
Training the future educators at the Best B.Ed College in Gurgaon
Gain Exceptional Business Expertise with Best B-School in Gurgaon
Best Undergraduate Courses to Study in India for a Promising Career
K.R. Mangalam University Admission Process 2023-24 Through KREE
Accelerate Your Career with Best University in Gurgaon for MBA
CTET 2023: Registration details for Central Teacher Eligibility Test
Develop Forensics Expertise with Best BSc Forensic Science Course in Delhi
Best Private Engineering College/University in Delhi NCR 2023
How to Choose a College or University: Key Factors to Count
Best BSc Hons Mathematics Scope: Career Options and Responsibilities
Best Courses After 12th Commerce – Professional Programmes & More
BBA in International Business 2023: Eligibility, Jobs and Salary
Integrated BBA MBA Course Details, Eligibility and Career options
BBA LLB Hons: Admission, Eligibility, Subjects, Scope and Jobs
What should You Do after completing BA in Political Science (honors)
How to Build a Career as an Automotive Designer/Car Designer?
Why studying Machine learning is a good career option after 12th
Ultimate Guide to CAT Exam: Admit card, Exam Date, Syllabus and Preparations
BA Honours in English: Course Details, Syllabus, Eligibility and Career Options
Career and Scopes after BCA with Artificial Intelligence and Data Science
Which Course Should I Choose After Completing 12th from Arts Stream
Why choose MCA: Course details, Eligibility, Benefits, Career Options and Salary
How to prepare for the CUET UG exam? Benefits, Syllabus and Study Material
Career, Scopes and Salary after B.Tech CSE with Specialisation in Cloud Computing
Career and Opportunities after completing your B.Tech Civil Engineering
What are the advantages of pursuing a B.Tech. in (CSE) with specialization in UX/UI
Planning to Pursue Integrated Course in B.Tech CSE with MBA?
Can a PCB Student do B.Tech in Computer Science Engineering in 2022
Why pursuing a BA (Hons.) – Chinese Degree can be a good choice for you?
Top Soft Skills That You Need to Develop for a Successful Career in 2022
Top Business Trends to Follow For a Successful Career In 2022
How to Build a Career in Stock Market in 2022 with Highest Paying Salary
B.Arch vs B.Des: Which Course to Choose for a Better Career?
How to Choose the Best Career Path: Machine Learning Engineer or Data Scientist
Top 20 Things Architects Can Do After B.Arch in India: A Must Read!
Get Better Job Opportunities with the Help of Top Colleges for MCA in Delhi NCR
K.R. Mangalam University Gears up to Sign MoU with Sputnik News Agency, Moscow
How Is Artificial Intelligence Shaping The Pharmacy Industry Of Today
The Emergence Of E-Commerce And E-Business In The Post-Pandemic World
The Role And Contribution Of Chemists In Improving The Overall Healthcare Scenario
5 Best Paying Jobs For Journalism & Mass Communicationgraduates
Clinical Psychology – Career Scope & Earning Potential In India
Challenges & Opportunities For Fashion Designers In The Post Covid World
The Invincible Role Of Medical & Allied Sciences Professionals Amid The Covid Crisis
The Emerging Role Of Information Technology In The Field Of Journalism
Indian Pharma Growing As The Largest Sector In Terms Of Employment & Revenue
The Importance Of Team Bonding For Management Professionals
Covid-19 Projects At KRMU: An Effort To Raise Awareness Among The Young Gen
Cybersecurity: A Much Sought-After Profession In Today’s Technology Oriented World
The Worth Of Industry-Vetted Management Training In 21st-Century Corporate World
Understanding The Twenty-First-Century Entrepreneurial Challenges
Why The World Of Fashion Needs Trendsetters Rather Than Followers?
Technological Trends Changing The Face Of Architecture Today
5 Significant Ways In Which The Industry Of Journalism Has Evolved Over The Years
Acquiring The Right Workforce Is The Key Requirement For Meeting Business Goals
The Vitality Of Application & Research-Based Learning For The 21st-Century Youth
How Will The Current Pandemic Change The Fashion Industry Worldwide?
Business Journalism – An Emerging Career Path For The 21st Century Youth
The Growing Use Of Business Analytics In Financial Services Industry
5 Reasons Why Studying Hotel Management Is A Great Choice In The Modern World
5 Tips For Beginners To Survive & Thrive In The Fashion Industry
Five Skills You Inevitably Need To Succeed As An Interior Designer
How Is The Advancing Technology Redesigning The Fashion Design Industry?
5 Myths About Human Resource Management That Need To Be Busted
Krmu’s Soa – Enabling The 21st Century Youth To Turn Into Agricultural Entrepreneurs
Krmu – Preparing Future Architects With A Global Perspective
Top Technical Skills That Are Highly Demanded in The Modern Job Market
Soil Science – Career Potential & Opportunities In India And Abroad
Key Skills You Need To Thrive In The Domain Of Hotel Management
The Significance Of Critical Thinking In Financial Management
The Role Of KRMU ICC In Establishing A Safe & Secure Environment In The Campus
What It Takes To Grab The Best Jobs In The Fashion Design World?
K.R. Mangalam – Building A Generation Of Creative Fashion Designers
What Makes Project-Based Learning Imperative For The Youth Of Today
KRMU’s Engineering Kitchen Inspiring The Youth To Shape A New World Of Innovation
The Impact Of Technological Advancements On The Efficiency Of Business Professionals
Experiential Projects – An Effective Way To Deep Rooted Management Education
KRMU’s Corporate Connect Aiding Students To Prove Their Mettle
Learn The True Art Of Innovation & Entrepreneurship At KRMU’s TIIE
KRMU To Establish A fully Functional Robotics Lab In Collaboration With IITBombay
Explore Engineering Kitchen – An Excellent Initiative Taken By KRMU
5 Reasons Why You Should Pursue A Degree In Journalism And Mass Communication
Five Reasons That Make Business Management One Among The Top Professions For Future
The Impact Of Artificial Intelligence And Iot On The Management Industry
Diverse Engineering Branches That Have Always Maintained Their Worth
Career Options That Will Be High In Demand In The Next Decade
KRMU – Creating A Culture Of Knowledge, Entrepreneurship, And Management Skills
Effective Marketing Management Can Help To Raise The Overall Value Of A Business
5 Invaluable Steps For Building An Excellent Professional Network
Priceless Qualities A Successful Legal Practitioner Needs To Treasure
Better Grades, Less Stress At School Of Law, K.R Mangalam University,Gurugram
Aesthetic And Logic, The Conflict Between Religion And Humanism In 21st Century
Best Ways For MBA Aspirants To Upgrade Their Communication Skills
How To Know If Journalism Is The Right Career Option For You
Tradition And Modernity Living Historical Quarters: Change And Continuity
Legal Profession One Of The Most Sought After Career Choices For Women Today
Dynamic Career Opportunities In Journalism Cultivated By Modern India
How Can Virtual Reality Help Pave Way For Transforming Architecture Education?
Top Questions Asked To Management Graduates In Placement Interviews
Wish To Make A Career In Ethical Hacking? Here’s All You Need To Know!
Future Career Perspectives Of Technical Education In India And Abroad
Why Is Personality Development An Utmost Need For Professional Success?
KRMU’S School Of Law – Strengthening The Legal Framework Of The Nation
The Importance Of Technology As A Teaching Aid In Higher Education
Top Business Lessons To Learn From Successful Businessmen From Across The World
Grooming The Students For The Current Trends In Medical And Allied Sciences
The Need For Skills Enhancement For The Competitive Corporate World
Tapping The Career Growth And Overseas Opportunities For Management Graduates
Significance Of Mentoring Programs Towards Holistic Development Of Students
KRMU – Delivering Education That Enables You To Lead The Competition

Learning Outcomes: Meaning, Examples & Objectives Difference
Today’s education is more than just memorising theories, lectures, and texts. Schools, universities, and even online courses now focus on what a student actually learns, not just what a teacher teaches. This shift has increased the importance of learning outcomes. It is a concept widely used in modern education, skill-based programmes, and professional training.
This blog explains what are learning outcomes, their examples, types, and how they differ from learning objectives, along with their importance in effective learning.
What are Learning Outcomes?
Learning outcomes are the information or abilities that students should have by the completion of a specific assignment, class, course, or programme. They help students:
- To recognise how such abilities and information will benefit them
- To emphasise the context and possible uses of knowledge and abilities
- To link education in a variety of settings
- By guiding them in directing review and assessment
Applying and integrating information is a key component of good learning outcomes. They describe how students will be able to use the material, both within and outside of the classroom, rather than concentrating on content covered.
Why are Learning Outcomes Important in Modern Education?
Learning outcomes play a key role in improving the quality of teaching and learning. Let’s explore how.
Benefits for Students
- Students are more engaged with their learning and the course material when they concentrate on applying the knowledge and skills they have learnt in the course and integrating them with other aspects of their lives.
- The focus on integration and transferable abilities increases student engagement by assisting students in making connections across courses and other types of information.
- Students are aware of the requirements and objectives of their evaluation.
Benefits for Teachers
- Creating these outcomes enables them to consider the course material and its possible uses, concentrating on the information and abilities that will be most useful to their students both now and in the future.
- They indicate effective assessment techniques.
- They give teachers the ability to establish the criteria by which the course’s effectiveness will be assessed.
Benefits for Institutions
- When a teacher evaluates a specific course or unit in light of upcoming assignments and the curriculum overall, it helps create a cohesive curriculum within a decentralised institution and guarantees that students are ready for work and learning in the future.
- They emphasise the application and integration of learning, which enhances student engagement, reveals opportunities for interdisciplinary study, and offers guidance and support to students with a wide range of prior academic preparation. These practices reflect and support the university’s contemporary nature and priorities.
- In addition to establishing frameworks for evaluating courses and programmes, they may help with curriculum and programme design, spot gaps or duplication in programme offerings, and define institutional, programmatic, and instructional priorities.
Also Read: Discover The Role Of Artificial Intelligence In Education
Difference Between Learning Outcomes and Objectives
Although often used together, learning objectives and outcomes are not the same. Let’s understand how.
| Comparison Point | Learning Objectives | Learning Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | What teachers will teach | What students will achieve |
| Measurability | Not always measurable | Always measurable |
| Orientation | Teacher-centred | Student-centred |
| Time | Before teaching begins | After course/lesson completion |
| Example | “The teacher will explain persuasive writing techniques.” | “Students will write a persuasive essay with correct formatting.” |
In simple words, ‘objective’ means ‘teaching goal’, and ‘outcome’ means ‘learning result’. Teachers plan objectives, but students demonstrate outcomes. This difference is important in professional education, where measurable results show whether teaching is effective.
Types of Learning Outcomes


Given below are the different types of learning outcomes.
Intellectual Capabilities
To get the best learning results using this kind of learning outcome, students must be able to fully comprehend the subject. The fundamental learning result that is anticipated of a student is knowledge acquisition.
Development of Cognitive Skills
This learning objective pushes students to consider, evaluate, and fully comprehend the significance of a particular idea before acting appropriately.
Exchange of Knowledge
Students must be able to impart important knowledge to others. Students are therefore expected to develop a value system of knowledge by first acquiring it and then disseminating it to the world as part of this learning objective.
Development of Motor Skills
Enhancing a student’s capacity to plan and execute appropriate physical actions is the focus of motor skill development. They have to strive for their physical and general well-being.
Personal Development of the Individual
The internal state of the learner’s behaviour is reflected in this learning result. The ultimate level of learning is personal development in terms of knowledge, abilities, and capacity to produce something for society. The student must be able to manage their personal and professional lives and react appropriately to real-life situations.
The ultimate level of learning is personal development in terms of knowledge, abilities, and capacity to produce something for society. The student must be able to manage their personal and professional lives and react appropriately to real-life situations.
Learning Outcomes Examples
Let’s examine some actual examples of these outcomes from various tasks.
Task 1: A new hire onboarding course
Learning outcome: Students are able to recognise circumstances in which corporate policies are applicable and explain the appropriate course of action.
This outcome demonstrates that students comprehend and can remember new ideas, reflecting knowledge or intellectual abilities.
Task 2: A mediation seminar for HR officers
Learning outcome: Students can use dispute resolution techniques in actual work situations.
This outcome evaluates performance and shows if students are able to apply what they have learnt.
Task 3: A new product management software training session conducted online
Learning outcome: Students are able to use the programme and describe its features.
This result emphasises competency, demonstrating that students are capable of demonstrating a useful ability.
Task 4: A virtual reality training course on machine component replacement
Learning outcome: Students are able to insert and remove machine parts appropriately while providing an explanation of their actions.
This outcome emphasises a learner’s capacity to carry out activities physically and is related to motor skills.
Task 5: A talk about organisational tactics
Learning outcome: By describing concrete actions, students may show how they will apply organisational techniques.
This outcome deals with verbal knowledge and calls on students to express and apply what they have learnt.
These examples highlight that these learning outcomes make education practical, measurable, and skill-orientated.
How to Identify Positive Learning Outcomes
A well-written learning outcome focuses on what the student can demonstrate in a tangible way once they have finished the learning task. Only observable learning outcomes are beneficial. Therefore, it should incorporate the learner’s learning behaviours, the proper evaluation technique, and the particular success criteria.
Examples of strong learning outcomes:
- The ability of students to recognise the situations in which each of the five forms of conflict management should be used.
- Learners will be able to navigate and complete all training modules using the company’s LMS.
- Students will be able to analyse marketing data and make graphs with it.
- Students will be able to write SEO-optimised copy using the techniques recommended by the organisation.
- Students may appropriately develop case studies using industry requirements.
- The autoclaves can be cleaned and operated correctly by learners.
Examples of weak learning outcomes:
- Students will comprehend how to handle conflicts.
- Students will be familiar with the company’s LMS.
- Students will value the application of marketing data.
- Students will be aware of the business’s SEO strategies.
- Students will comprehend the components of a case study.
- Students will get knowledge about autoclaves.
To put it briefly, weak learning outcomes are ambiguous and challenging to evaluate, whereas strong ones are quantifiable and practical.
How to Create Learning Outcomes that Work for Every Learner
Whether you are in a classroom or a corporate environment, having explicit learning goals is crucial for effective training and education.
This is a methodical strategy for developing successful learning outcomes in many contexts, as mentioned below.
Determine the Learning Activity’s Goal
Make sure you understand the goal of the training session or class before determining results. The goal lays the groundwork for quantifiable results, whether it be skill development, compliance training, or the introduction of new ideas.
Describe What Success Means to Students
When creating a learning objective, consider what proficient students will be able to accomplish at the conclusion of the course or training. Consider observable behaviours. Will students be able to recognise, clarify, illustrate, or apply an idea, for instance?
Think About Several Forms of Education
Learning is more than just learning information by heart. Depending on the training or educational setting, learners may need to acquire physical skills, cognitive techniques, or intellectual abilities.
Make Sure the Results are Quantifiable
Effective results must be measurable via testing or observation. Can students successfully show their knowledge, do an assignment, or use a skill?
Align Results with Practical Uses
According to research, performance-based assessments—in which students use their knowledge or abilities in practical situations—are frequently more successful than standard knowledge examinations in gauging employee learning results.
Make results applicable by relating them to real-world applications. This guarantees that learning is useful outside of the classroom or training session and boosts engagement.
How Learning Outcomes Improve Effective Learning
Effective learning means students understand concepts deeply and can apply them—not just memorise. These outcomes directly support this by:
- Giving clear learning expectations
- Connecting teaching to real-life skills
- Making assessment more meaningful
- Helping students stay focused and motivated
- Allowing teachers to design better teaching strategies
For example, if a learning outcome says, “Students will create a multimedia presentation on climate change.”
It requires research, creativity, critical thinking, and communication—all key elements of effective learning.
Course Outcomes and Their Role
At the university level, every subject or course has a defined Course Outcome(s) (COs).
A course outcome explains what a student will achieve after completing the entire subject or semester.
Example of COs:
- Apply programming logic to solve real problems
- Understand marketing principles and apply them to case studies
- Conduct laboratory experiments and analyse results
Course outcomes ensure learning is job-orientated, practical, and aligned with industry requirements.
Teaching Objective
Teaching objectives guide teachers in planning lessons. They explain what a teacher intends to cover:
- Explain the chapter
- Introduce new concepts
- Conduct activities
- Provide notes and assignments
But the outcome shows whether these efforts worked. Teaching objectives lead to learning objectives, which in turn lead to learning outcomes.
Role of K.R. Mangalam University (KRMU) in Outcome-Based Education
Below are the points that show how K.R. Mangalam University ensures strong learning outcomes. The university offers:
- Industry-focused curriculum
- Practical training, labs, simulations, internships
- Project-based learning and real-world exposure
- Continuous assessment to check learning progress
- Faculty mentoring and skill development sessions
As a result, students don’t just learn theory, but they also gain practical knowledge, employability skills, communication abilities, and confidence for career success.
Conclusion
We have understood how and why learning outcomes are an essential part of modern education. They provide clarity, direction, and measurable achievements for both teachers and students. Whether in schools, universities, or corporate training, they ensure that knowledge turns into skills and learning leads to real progress. Students become more confident and goal-orientated, teachers plan better lessons and employers get industry-ready professionals.
With outcome-based learning, education becomes meaningful, skill-driven, and future-focused—and this is exactly what institutes like KRMU aim to deliver.
Also Read: What Is The Importance Of Inclusive Education
FAQs
Q1. What are learning outcomes?
Learning outcomes are measurable statements describing what a student will know or be able to do after completing a course or lesson.
Q2. What is the difference between learning outcomes and objectives?
Learning objectives are teaching goals, while learning outcomes are measurable results of what students actually learn.
Q3. Where are learning outcomes used?
Learning outcomes are used in schools, colleges, skill training programmes, online courses, and corporate training.
Q4. Why are learning outcomes important?
They improve teaching quality, student performance, and assessment.
Recent Post
All India Forensic Science Entrance Test (AIFSET-2026) Details and Eligibility
Explore the Top Artificial Intelligence University in India
BBA HR Management Syllabus: Semester-Wise Detailed Curriculum
Best AI Colleges in India 2025: Rankings, Fees, Admissions & Placement Insights
Best Universities in Delhi NCR 2025: Rankings, Admissions & Fees Guide
Top Engineering Colleges in Gurgaon 2025-26: Admission, Fees & Placement Guide
Explore the Best Courses After Graduation for High Salary
BSc Data Science: Syllabus, Careers, and Data Science Course
Understanding the Difference Between Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Is Data Science a Good Career Choice? Salary, Scope & Future Growth Explained
Integrated Course After 12th: Complete Guide, List and Benefits
Moot Court for Law Students: Its Importance and Objectives
CAT 2025: Exam Date, Eligibility, Syllabus, Registration & Preparation Tips
Explore the Best College for MBA in Marketing in Delhi NCR
Career Guidance and Counselling: Expert Support for a Successful Future
Importance of Internships: Boost Your Career with Real-World Experience
CUET Result 2025 Out: Check Scores, Cut-Offs & What to Do Next
Pursue Bachelor’s Degree in Journalism & Mass Communication at KRMU
BCA Course After 12th: Best College, Fees, Curriculum and More
BBA in Digital Marketing: Eligibility, Subjects, Fee and Scope
Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering: Eligibility, Admission and Fee Details
B Pharmacy Admission 2025: Course Details | Eligibility | Career
Is B.Sc. Computer Science Worth It? Salary, Scope & Future Prospects
KRMU: The Destination to Become a Future-Ready Software Engineer
Ph.D. Pharmaceutical Sciences: Course Details and Admission Process
Why KRMU is the Best College for BCom Hons. in Gurugram, Delhi NCR
JEE Mains 2025 Exam Date: Syllabus, Last date, Registration Date
Career After MA English: High Paying Jobs and Government Roles
B.Sc. Full Form Explained: Courses, Eligibility, Jobs & Admission
Why K.R. Mangalam University Is The Best Fine Arts University in India
Benefits of a Culinary Arts Bachelor Degree for Aspiring Chefs
Architecture Careers In India: Your Path To A Successful Future
Is NTA CUET UG Score Mandatory For Admission In All Universities
Choosing The Best B Sc Courses After 12th: A Detailed Guide To Your Future
Data Science and Artificial Intelligence: Revolutionising the Digital Age
Exploring Top Career Options For Commerce Students After The 12th
Exploring The Best Course After B Com To Elevate Future Prospects
The Difference between BE and BTech: Everything you need to know
Exploring Jobs After BSc Chemistry: Private And Government Jobs
What Are Some of The Best Professional Courses After 12th Class
Architecture Courses after 12th: Duration, Eligibility, Career Options
Why KRMU Is Considered One Of The Best BSc Agriculture Colleges In India?
A Complete Guide On Full Stack Development: Career Paths/Eligibility/Duration
Why KRMU Is Considered One Of The Best Hotel Management Colleges In India
Hotel Management Course Fees in Private College: What You Need to Know
Everything You Need to Know About Integrating Dual Degree Programs
Textile Design Course, Eligibility and Career Opportunities
Physiotherapy Course Fees: Career Paths/Eligibility Criteria/Top Colleges
Exploring BJMC Colleges in Delhi: Your Comprehensive Guide
A Comprehensive Guide B Pharm Duration, Syllabus, Job Opportunities
BCA Full Form And Subjects- Comprehensive Understanding Of BCA
Complete Guide of B Sc Agriculture Course Duration, Admission Process, Fees
A Detailed Guide On How To Become A Fashion Designer After 12th
Navigating Sustainability Trends: Preparing Students for Corporate Priorities in 2024
What Can I Do After a BA? Exploring Career Options for Bachelor of Arts Graduates
List Of Top Career Options After B.Tech Computer Science & Engineering
How to Choose the Right 12th Commerce Courses for Your Salary?
K.R. Mangalam University: A Leading University For Comprehensive Excellence
Understanding BBA Travel & Tourism: A Gateway To A Thriving Future
A Journey through K.R. Mangalam University’s as a Student of B.A. Honours Psychology
Why Choose B Tech Cyber Security: Learn Eligibility/Benefits/Career/College
List of B.Tech Courses: Various Specialisations/Eligibility Criteria/Careers
Benefits of Pursuing An MBA After BA: Career/Specialisations/Entrance Exam
Essential Guide On KR Mangalam University Scholarship For 2024-25
Everything You Need To Know About Architecture And Design in 2024
Exploring the UX/UI Race in B.Tech. Computer Science & Engineering
Exploring the UX/UI Race in B.Tech. Computer Science & Engineering
The Rising Demand For Management Professionals In The Country
B.Tech Computer Science Course: Eligibility, Syllabus, Exams, Fees, Scope
Exploring a BBA in Finance: Your Comprehensive Guide to a Promising Career Path
Compelling Reasons to Choose a BBA Program in Travel and Tourism
BA Political Science Honours: Your Path to Political Insight
Beyond Fashion Designing: Exploring the Creative World of B.A. Arts
Unlocking the Path to Success: Your Thriving Career in Cyber Security
Soaring to New Heights: Apeejay Professor Takes Flight as Certified Drone Flyer
D Pharmacy Course Details: Eligibility, Admissions & Subjects
The Art of Public Speaking: Tips for Confident Presentations
Advancing Your Career: Pursuing Diploma Courses After 10th Grade
Computer Science Engineering: Unraveling the Realm of Technology and Innovation
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Data Science Course for Your Career
Internship and Practical Training Opportunities for B.Com (Honours) Students
Exploring Career Scope of Pharmacology: A Promising Pathway
The Rise of Fintech: Revolutionizing India’s Financial Landscape
The Advancement Postgraduate Courses in India Career Development
Mastering Time Management: A Key to Success in Work and Life
Understanding the Difference Between Psychologist and Psychiatrist
Career in Fashion Designing: Full Guide from Start to Destination
Diploma Course vs Degree Course: Exploring the Pros and Cons
Must Watch Movies and Web series For Forensic Science Student
Exploring a Career in Criminal Law: An In-Depth Guide to LLB Criminal Law
Unveiling the Role of a Supply Chain Analyst: A Path to Success
Comparing CSE and IT: Unveiling Distinctions and Career Opportunities
Exploring the Educational Landscape: Top Universities in Gurgaon
Architecture Course: Guide to Becoming an Architect in India
Traditional Marketing vs Digital Marketing: Exploring their Pros and Cons
The Basics of B Tech: What You Need to Know to Pursue a Degree in Technology
Is Pursuing MBA After Engineering an Excellent Career Choice
How To Become An Interior Designer in India: Qualification & Career Scopes
Exploring the Benefits of an International Accounting and Finance Course
BA LLB (Hons): A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Program
5 Full Stack Web Development Course Lessons from the Professionals
Training the future educators at the Best B.Ed College in Gurgaon
Gain Exceptional Business Expertise with Best B-School in Gurgaon
Best Undergraduate Courses to Study in India for a Promising Career
K.R. Mangalam University Admission Process 2023-24 Through KREE
Accelerate Your Career with Best University in Gurgaon for MBA
CTET 2023: Registration details for Central Teacher Eligibility Test
Develop Forensics Expertise with Best BSc Forensic Science Course in Delhi
Best Private Engineering College/University in Delhi NCR 2023
How to Choose a College or University: Key Factors to Count
Best BSc Hons Mathematics Scope: Career Options and Responsibilities
Best Courses After 12th Commerce – Professional Programmes & More
BBA in International Business 2023: Eligibility, Jobs and Salary
Integrated BBA MBA Course Details, Eligibility and Career options
BBA LLB Hons: Admission, Eligibility, Subjects, Scope and Jobs
What should You Do after completing BA in Political Science (honors)
How to Build a Career as an Automotive Designer/Car Designer?
Why studying Machine learning is a good career option after 12th
Ultimate Guide to CAT Exam: Admit card, Exam Date, Syllabus and Preparations
BA Honours in English: Course Details, Syllabus, Eligibility and Career Options
Career and Scopes after BCA with Artificial Intelligence and Data Science
Which Course Should I Choose After Completing 12th from Arts Stream
Why choose MCA: Course details, Eligibility, Benefits, Career Options and Salary
How to prepare for the CUET UG exam? Benefits, Syllabus and Study Material
Career, Scopes and Salary after B.Tech CSE with Specialisation in Cloud Computing
Career and Opportunities after completing your B.Tech Civil Engineering
What are the advantages of pursuing a B.Tech. in (CSE) with specialization in UX/UI
Planning to Pursue Integrated Course in B.Tech CSE with MBA?
Can a PCB Student do B.Tech in Computer Science Engineering in 2022
Why pursuing a BA (Hons.) – Chinese Degree can be a good choice for you?
Top Soft Skills That You Need to Develop for a Successful Career in 2022
Top Business Trends to Follow For a Successful Career In 2022
How to Build a Career in Stock Market in 2022 with Highest Paying Salary
B.Arch vs B.Des: Which Course to Choose for a Better Career?
How to Choose the Best Career Path: Machine Learning Engineer or Data Scientist
Top 20 Things Architects Can Do After B.Arch in India: A Must Read!
Get Better Job Opportunities with the Help of Top Colleges for MCA in Delhi NCR
K.R. Mangalam University Gears up to Sign MoU with Sputnik News Agency, Moscow
How Is Artificial Intelligence Shaping The Pharmacy Industry Of Today
The Emergence Of E-Commerce And E-Business In The Post-Pandemic World
The Role And Contribution Of Chemists In Improving The Overall Healthcare Scenario
5 Best Paying Jobs For Journalism & Mass Communicationgraduates
Clinical Psychology – Career Scope & Earning Potential In India
Challenges & Opportunities For Fashion Designers In The Post Covid World
The Invincible Role Of Medical & Allied Sciences Professionals Amid The Covid Crisis
The Emerging Role Of Information Technology In The Field Of Journalism
Indian Pharma Growing As The Largest Sector In Terms Of Employment & Revenue
The Importance Of Team Bonding For Management Professionals
Covid-19 Projects At KRMU: An Effort To Raise Awareness Among The Young Gen
Cybersecurity: A Much Sought-After Profession In Today’s Technology Oriented World
The Worth Of Industry-Vetted Management Training In 21st-Century Corporate World
Understanding The Twenty-First-Century Entrepreneurial Challenges
Why The World Of Fashion Needs Trendsetters Rather Than Followers?
Technological Trends Changing The Face Of Architecture Today
5 Significant Ways In Which The Industry Of Journalism Has Evolved Over The Years
Acquiring The Right Workforce Is The Key Requirement For Meeting Business Goals
The Vitality Of Application & Research-Based Learning For The 21st-Century Youth
How Will The Current Pandemic Change The Fashion Industry Worldwide?
Business Journalism – An Emerging Career Path For The 21st Century Youth
The Growing Use Of Business Analytics In Financial Services Industry
5 Reasons Why Studying Hotel Management Is A Great Choice In The Modern World
5 Tips For Beginners To Survive & Thrive In The Fashion Industry
Five Skills You Inevitably Need To Succeed As An Interior Designer
How Is The Advancing Technology Redesigning The Fashion Design Industry?
5 Myths About Human Resource Management That Need To Be Busted
Krmu’s Soa – Enabling The 21st Century Youth To Turn Into Agricultural Entrepreneurs
Krmu – Preparing Future Architects With A Global Perspective
Top Technical Skills That Are Highly Demanded in The Modern Job Market
Soil Science – Career Potential & Opportunities In India And Abroad
Key Skills You Need To Thrive In The Domain Of Hotel Management
The Significance Of Critical Thinking In Financial Management
The Role Of KRMU ICC In Establishing A Safe & Secure Environment In The Campus
What It Takes To Grab The Best Jobs In The Fashion Design World?
K.R. Mangalam – Building A Generation Of Creative Fashion Designers
What Makes Project-Based Learning Imperative For The Youth Of Today
KRMU’s Engineering Kitchen Inspiring The Youth To Shape A New World Of Innovation
The Impact Of Technological Advancements On The Efficiency Of Business Professionals
Experiential Projects – An Effective Way To Deep Rooted Management Education
KRMU’s Corporate Connect Aiding Students To Prove Their Mettle
Learn The True Art Of Innovation & Entrepreneurship At KRMU’s TIIE
KRMU To Establish A fully Functional Robotics Lab In Collaboration With IITBombay
Explore Engineering Kitchen – An Excellent Initiative Taken By KRMU
5 Reasons Why You Should Pursue A Degree In Journalism And Mass Communication
Five Reasons That Make Business Management One Among The Top Professions For Future
The Impact Of Artificial Intelligence And Iot On The Management Industry
Diverse Engineering Branches That Have Always Maintained Their Worth
Career Options That Will Be High In Demand In The Next Decade
KRMU – Creating A Culture Of Knowledge, Entrepreneurship, And Management Skills
Effective Marketing Management Can Help To Raise The Overall Value Of A Business
5 Invaluable Steps For Building An Excellent Professional Network
Priceless Qualities A Successful Legal Practitioner Needs To Treasure
Better Grades, Less Stress At School Of Law, K.R Mangalam University,Gurugram
Aesthetic And Logic, The Conflict Between Religion And Humanism In 21st Century
Best Ways For MBA Aspirants To Upgrade Their Communication Skills
How To Know If Journalism Is The Right Career Option For You
Tradition And Modernity Living Historical Quarters: Change And Continuity
Legal Profession One Of The Most Sought After Career Choices For Women Today
Dynamic Career Opportunities In Journalism Cultivated By Modern India
How Can Virtual Reality Help Pave Way For Transforming Architecture Education?
Top Questions Asked To Management Graduates In Placement Interviews
Wish To Make A Career In Ethical Hacking? Here’s All You Need To Know!
Future Career Perspectives Of Technical Education In India And Abroad
Why Is Personality Development An Utmost Need For Professional Success?
KRMU’S School Of Law – Strengthening The Legal Framework Of The Nation
The Importance Of Technology As A Teaching Aid In Higher Education
Top Business Lessons To Learn From Successful Businessmen From Across The World
Grooming The Students For The Current Trends In Medical And Allied Sciences
The Need For Skills Enhancement For The Competitive Corporate World
Tapping The Career Growth And Overseas Opportunities For Management Graduates
Significance Of Mentoring Programs Towards Holistic Development Of Students
KRMU – Delivering Education That Enables You To Lead The Competition
Error: Contact form not found.
Learning Outcomes: Meaning, Examples & Objectives Difference


Blog Content
Today’s education is more than just memorising theories, lectures, and texts. Schools, universities, and even online courses now focus on what a student actually learns, not just what a teacher teaches. This shift has increased the importance of learning outcomes. It is a concept widely used in modern education, skill-based programmes, and professional training.
This blog explains what are learning outcomes, their examples, types, and how they differ from learning objectives, along with their importance in effective learning.
What are Learning Outcomes?
Learning outcomes are the information or abilities that students should have by the completion of a specific assignment, class, course, or programme. They help students:
- To recognise how such abilities and information will benefit them
- To emphasise the context and possible uses of knowledge and abilities
- To link education in a variety of settings
- By guiding them in directing review and assessment
Applying and integrating information is a key component of good learning outcomes. They describe how students will be able to use the material, both within and outside of the classroom, rather than concentrating on content covered.
Why are Learning Outcomes Important in Modern Education?
Learning outcomes play a key role in improving the quality of teaching and learning. Let’s explore how.
Benefits for Students
- Students are more engaged with their learning and the course material when they concentrate on applying the knowledge and skills they have learnt in the course and integrating them with other aspects of their lives.
- The focus on integration and transferable abilities increases student engagement by assisting students in making connections across courses and other types of information.
- Students are aware of the requirements and objectives of their evaluation.
Benefits for Teachers
- Creating these outcomes enables them to consider the course material and its possible uses, concentrating on the information and abilities that will be most useful to their students both now and in the future.
- They indicate effective assessment techniques.
- They give teachers the ability to establish the criteria by which the course’s effectiveness will be assessed.
Benefits for Institutions
- When a teacher evaluates a specific course or unit in light of upcoming assignments and the curriculum overall, it helps create a cohesive curriculum within a decentralised institution and guarantees that students are ready for work and learning in the future.
- They emphasise the application and integration of learning, which enhances student engagement, reveals opportunities for interdisciplinary study, and offers guidance and support to students with a wide range of prior academic preparation. These practices reflect and support the university’s contemporary nature and priorities.
- In addition to establishing frameworks for evaluating courses and programmes, they may help with curriculum and programme design, spot gaps or duplication in programme offerings, and define institutional, programmatic, and instructional priorities.
Also Read: Discover The Role Of Artificial Intelligence In Education
Difference Between Learning Outcomes and Objectives
Although often used together, learning objectives and outcomes are not the same. Let’s understand how.
| Comparison Point | Learning Objectives | Learning Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | What teachers will teach | What students will achieve |
| Measurability | Not always measurable | Always measurable |
| Orientation | Teacher-centred | Student-centred |
| Time | Before teaching begins | After course/lesson completion |
| Example | “The teacher will explain persuasive writing techniques.” | “Students will write a persuasive essay with correct formatting.” |
In simple words, ‘objective’ means ‘teaching goal’, and ‘outcome’ means ‘learning result’. Teachers plan objectives, but students demonstrate outcomes. This difference is important in professional education, where measurable results show whether teaching is effective.
Types of Learning Outcomes


Given below are the different types of learning outcomes.
Intellectual Capabilities
To get the best learning results using this kind of learning outcome, students must be able to fully comprehend the subject. The fundamental learning result that is anticipated of a student is knowledge acquisition.
Development of Cognitive Skills
This learning objective pushes students to consider, evaluate, and fully comprehend the significance of a particular idea before acting appropriately.
Exchange of Knowledge
Students must be able to impart important knowledge to others. Students are therefore expected to develop a value system of knowledge by first acquiring it and then disseminating it to the world as part of this learning objective.
Development of Motor Skills
Enhancing a student’s capacity to plan and execute appropriate physical actions is the focus of motor skill development. They have to strive for their physical and general well-being.
Personal Development of the Individual
The internal state of the learner’s behaviour is reflected in this learning result. The ultimate level of learning is personal development in terms of knowledge, abilities, and capacity to produce something for society. The student must be able to manage their personal and professional lives and react appropriately to real-life situations.
The ultimate level of learning is personal development in terms of knowledge, abilities, and capacity to produce something for society. The student must be able to manage their personal and professional lives and react appropriately to real-life situations.
Learning Outcomes Examples
Let’s examine some actual examples of these outcomes from various tasks.
Task 1: A new hire onboarding course
Learning outcome: Students are able to recognise circumstances in which corporate policies are applicable and explain the appropriate course of action.
This outcome demonstrates that students comprehend and can remember new ideas, reflecting knowledge or intellectual abilities.
Task 2: A mediation seminar for HR officers
Learning outcome: Students can use dispute resolution techniques in actual work situations.
This outcome evaluates performance and shows if students are able to apply what they have learnt.
Task 3: A new product management software training session conducted online
Learning outcome: Students are able to use the programme and describe its features.
This result emphasises competency, demonstrating that students are capable of demonstrating a useful ability.
Task 4: A virtual reality training course on machine component replacement
Learning outcome: Students are able to insert and remove machine parts appropriately while providing an explanation of their actions.
This outcome emphasises a learner’s capacity to carry out activities physically and is related to motor skills.
Task 5: A talk about organisational tactics
Learning outcome: By describing concrete actions, students may show how they will apply organisational techniques.
This outcome deals with verbal knowledge and calls on students to express and apply what they have learnt.
These examples highlight that these learning outcomes make education practical, measurable, and skill-orientated.
How to Identify Positive Learning Outcomes
A well-written learning outcome focuses on what the student can demonstrate in a tangible way once they have finished the learning task. Only observable learning outcomes are beneficial. Therefore, it should incorporate the learner’s learning behaviours, the proper evaluation technique, and the particular success criteria.
Examples of strong learning outcomes:
- The ability of students to recognise the situations in which each of the five forms of conflict management should be used.
- Learners will be able to navigate and complete all training modules using the company’s LMS.
- Students will be able to analyse marketing data and make graphs with it.
- Students will be able to write SEO-optimised copy using the techniques recommended by the organisation.
- Students may appropriately develop case studies using industry requirements.
- The autoclaves can be cleaned and operated correctly by learners.
Examples of weak learning outcomes:
- Students will comprehend how to handle conflicts.
- Students will be familiar with the company’s LMS.
- Students will value the application of marketing data.
- Students will be aware of the business’s SEO strategies.
- Students will comprehend the components of a case study.
- Students will get knowledge about autoclaves.
To put it briefly, weak learning outcomes are ambiguous and challenging to evaluate, whereas strong ones are quantifiable and practical.
How to Create Learning Outcomes that Work for Every Learner
Whether you are in a classroom or a corporate environment, having explicit learning goals is crucial for effective training and education.
This is a methodical strategy for developing successful learning outcomes in many contexts, as mentioned below.
Determine the Learning Activity’s Goal
Make sure you understand the goal of the training session or class before determining results. The goal lays the groundwork for quantifiable results, whether it be skill development, compliance training, or the introduction of new ideas.
Describe What Success Means to Students
When creating a learning objective, consider what proficient students will be able to accomplish at the conclusion of the course or training. Consider observable behaviours. Will students be able to recognise, clarify, illustrate, or apply an idea, for instance?
Think About Several Forms of Education
Learning is more than just learning information by heart. Depending on the training or educational setting, learners may need to acquire physical skills, cognitive techniques, or intellectual abilities.
Make Sure the Results are Quantifiable
Effective results must be measurable via testing or observation. Can students successfully show their knowledge, do an assignment, or use a skill?
Align Results with Practical Uses
According to research, performance-based assessments—in which students use their knowledge or abilities in practical situations—are frequently more successful than standard knowledge examinations in gauging employee learning results.
Make results applicable by relating them to real-world applications. This guarantees that learning is useful outside of the classroom or training session and boosts engagement.
How Learning Outcomes Improve Effective Learning
Effective learning means students understand concepts deeply and can apply them—not just memorise. These outcomes directly support this by:
- Giving clear learning expectations
- Connecting teaching to real-life skills
- Making assessment more meaningful
- Helping students stay focused and motivated
- Allowing teachers to design better teaching strategies
For example, if a learning outcome says, “Students will create a multimedia presentation on climate change.”
It requires research, creativity, critical thinking, and communication—all key elements of effective learning.
Course Outcomes and Their Role
At the university level, every subject or course has a defined Course Outcome(s) (COs).
A course outcome explains what a student will achieve after completing the entire subject or semester.
Example of COs:
- Apply programming logic to solve real problems
- Understand marketing principles and apply them to case studies
- Conduct laboratory experiments and analyse results
Course outcomes ensure learning is job-orientated, practical, and aligned with industry requirements.
Teaching Objective
Teaching objectives guide teachers in planning lessons. They explain what a teacher intends to cover:
- Explain the chapter
- Introduce new concepts
- Conduct activities
- Provide notes and assignments
But the outcome shows whether these efforts worked. Teaching objectives lead to learning objectives, which in turn lead to learning outcomes.
Role of K.R. Mangalam University (KRMU) in Outcome-Based Education
Below are the points that show how K.R. Mangalam University ensures strong learning outcomes. The university offers:
- Industry-focused curriculum
- Practical training, labs, simulations, internships
- Project-based learning and real-world exposure
- Continuous assessment to check learning progress
- Faculty mentoring and skill development sessions
As a result, students don’t just learn theory, but they also gain practical knowledge, employability skills, communication abilities, and confidence for career success.
Conclusion
We have understood how and why learning outcomes are an essential part of modern education. They provide clarity, direction, and measurable achievements for both teachers and students. Whether in schools, universities, or corporate training, they ensure that knowledge turns into skills and learning leads to real progress. Students become more confident and goal-orientated, teachers plan better lessons and employers get industry-ready professionals.
With outcome-based learning, education becomes meaningful, skill-driven, and future-focused—and this is exactly what institutes like KRMU aim to deliver.
Also Read: What Is The Importance Of Inclusive Education
FAQs
Q1. What are learning outcomes?
Learning outcomes are measurable statements describing what a student will know or be able to do after completing a course or lesson.
Q2. What is the difference between learning outcomes and objectives?
Learning objectives are teaching goals, while learning outcomes are measurable results of what students actually learn.
Q3. Where are learning outcomes used?
Learning outcomes are used in schools, colleges, skill training programmes, online courses, and corporate training.
Q4. Why are learning outcomes important?
They improve teaching quality, student performance, and assessment.
