Full Form of LLB and LLM: Are you in search of a post-12th-grade degree course? There are so many professional courses that finding one is quite exciting and daunting. If you are passionate about legal education and have a keen eye for details, LLB and LLM are the two courses you need to consider.
You may or may not have heard these words before, but LLB and LLM are two of the pivotal courses for legal education. Both courses are designed to be the bedrock of legal qualifications and specialization. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll discuss the full form of LLB and LLM and understand both courses in detail.
What is LLB?
LLB course is a 3-year programme that offers a comprehensive understanding of various aspects of law. The LLB full form is Bachelor of Laws or Bachelor of Legislative Laws. The course syllabus covers various key courses like contract law, criminal law, civil law, property law and constitutional law.
The course opens various opportunities for students in the legal and non-legal fields. After earning the LLB degree, students can pursue careers in legal journalism, corporate law, civil services and academia.
Core Subjects and Skills
The LLB programme comprises a broad range of subjects like criminal law, labour law, constitutional law, law of evidence, human rights law etc. These courses are well-designed for students to create a well-rounded legal perspective. Also, the course focuses on critical skills such as legal thinking and argumentation.
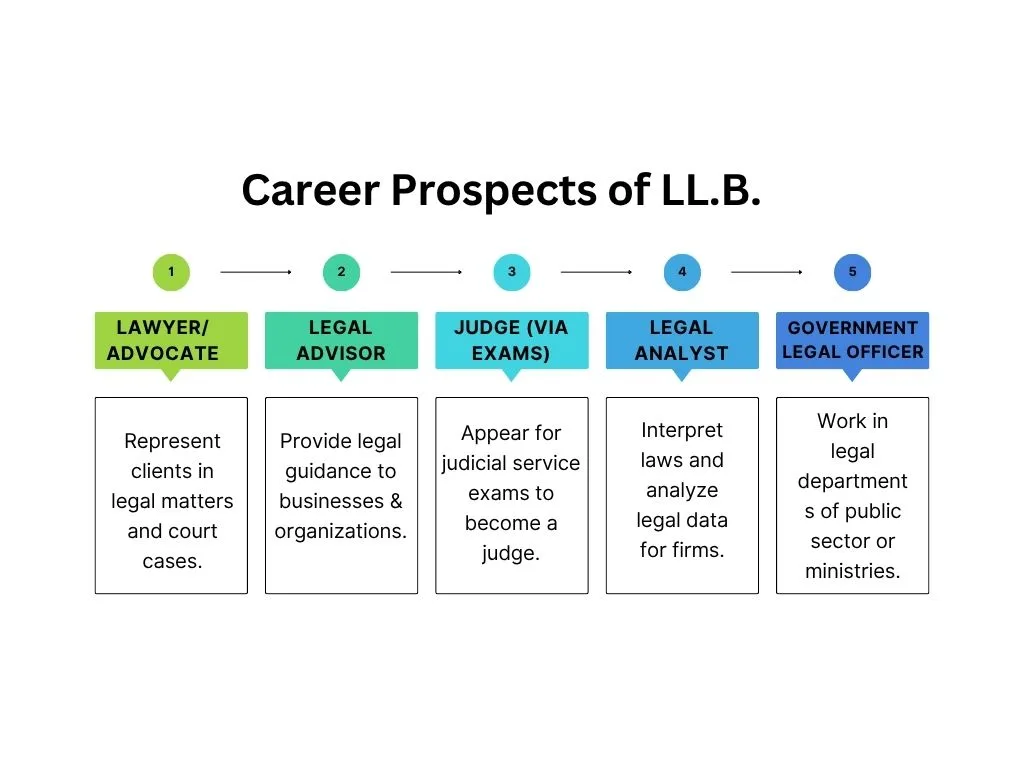
Career Prospects
After completing the course, students can go for the practice of solicitors or barristers. Apart from these options, students can also go for the role of corporate law, legal consultancy, or public service.
What is LLM?
LLM is a postgraduate degree programme for those students who have already completed their undergraduate studies in law. LLM’s full form is Legum Magister, a Latin word which means continuation of legal education.
The LLM is a two-year master’s degree programme offering specialized legal education in fields like international law, human rights law and corporate law. The LLM program gives a broad overview to students about the law and enhances their expertise and professional credentials.
Core Subjects
The LLM programme gives students an in-depth knowledge of legal research and prepares them for practical skills. During the programme, students get a foundational understanding of the law. The programme comprises subjects like Constitutional Law, Jurisprudence, Contract Law, Tort Law, Criminal Law, Family Law, and Administrative Law.
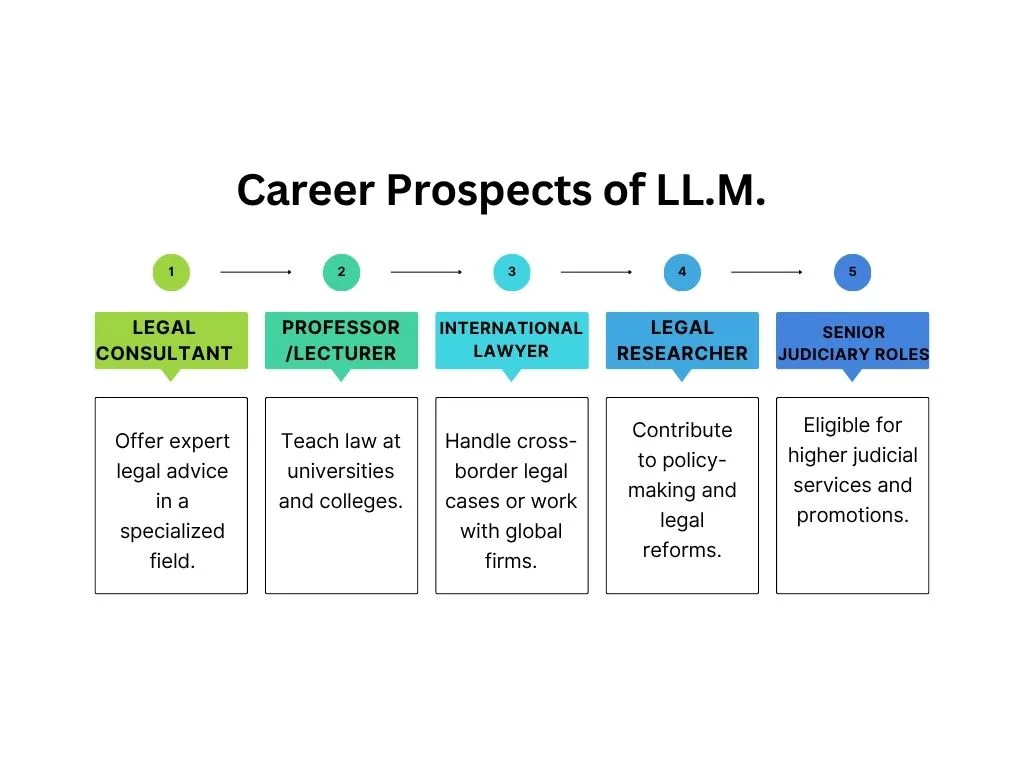
Career Prospects
After completing the LLM course, there are several opportunities open for students. The LLM degree gives students a higher level of position in law firms. After completing the programme, students can pursue careers as advocates, district and session judges, notaries, solicitor, court reporters etc.
Also Read: LLB Admission: Know Its Process, Eligibility and More
How Many Years is a Law Course?
The duration of a law course varies depending on the degree and country in which one is chosen to study. However, in India, the duration of LLB is of three years and the integrated LLB is 5 years. The integrated course focuses on the study of graduation along with the in-depth study of law & legislature.
After completing the LLB course, students can study further a master’s degree with LLM. The duration of the LLM course is 2 years and it focuses on advanced, specialized legal education.
Comparing LLB and LLM
The LLB and LLM are two distinguished degrees in Legal Education. The full forms of llb and llm are Bachelor of Laws and Master of Laws. LLB is an undergraduate programme, whereas the LLM is a master’s degree programme. Besides, LLB is the first step of students in the legal study whereas the LLM is a advanced programme sepecialise student in specific areas of law or pursue advanced legal studies.
Duration and Focus
The duration of LLB and LLM are different because the LLB programme is 3 years and LLB lasts for 2 years. LLM programme focuses on fundamental understanding of law whereas LLM is designed for specialized, in-depth legal study.
Level of Specialization
As compared to LLB, the level of LLM is higher because it allows students to focus on specific fields like corporate governance, international law, human rights and intellectual property. Studying LLM after LLB is an important part that allows students to advance their legal careers or transition into niche legal fields.
| Criteria |
LLB
|
LLM
|
|
Full Form
|
Bachelor of Law
|
Master of Law
|
|
Level
|
Undergraduate Degree
|
Postgraduate Degree
|
|
Duration
|
3 years (for graduates) or 5 years (integrated)
|
2 years
|
|
Eligibility
|
Completion of higher secondary education (for integrated) or a Bachelor’s degree in any field
|
Completion of LLB or equivalent law degree
|
|
Focus
|
Provides foundational legal knowledge and prepares students for law practice
|
Offers specialisation in specific areas of law
|
|
Career Path
|
Entry-level positions in legal practice, judiciary, and corporate sectors
|
Advanced roles in law, academia, research, and specialised legal practice
|
|
Objective
|
To equip students with fundamental legal concepts and prepare them for legal professions
|
To provide advanced legal expertise and research opportunities in specialised fields
|
|
Common Specialisations
|
General law, Constitutional law, Criminal law, Corporate law
|
International law, Human rights law, Taxation law, Corporate law
|
|
Post-Degree Options
|
Practice as a lawyer, judge, or legal consultant
|
Academia, legal research, international organisations, higher judiciary roles
|
Why Choose Law as a Career?
The legal profession in India has evolved beyond courtrooms and litigation. Today, law graduates work in diverse areas such as corporate firms, international organizations, judiciary, government services, NGOs, legal research, policy think tanks, and more. A career in law is not only intellectually challenging but also socially impactful. Whether you choose LLB or go further with LLM, the legal field offers job stability, high earning potential, and the opportunity to advocate for justice.
Specialisations and Emerging Fields
Now Law as a profession is no longer limited to traditional roles like litigation or civil law. With globalization, technological advancements, and evolving socio-economic needs, several new specializations have emerged that offer exciting opportunities for LLB and LLM graduates:
- Cyber Law: With the surge in online transactions, cybercrimes, and data privacy issues, cyber law specialists are in high demand to regulate and protect digital spaces.
- Intellectual Property Rights (IPR): From patents to trademarks, IPR lawyers play a vital role in safeguarding creativity and innovation in industries like technology, pharmaceuticals, and entertainment.
- Environmental Law: With increasing global focus on climate change and sustainability, this field deals with issues like environmental protection, conservation policies, and corporate compliance with green laws.
- Human Rights Law: Specialists work on advocacy, litigation, and policy reforms to protect fundamental rights and promote justice both nationally and internationally.
- Corporate & Commercial Law: A lucrative field where lawyers deal with mergers, acquisitions, corporate governance, and contract management in the business sector.
- International Trade & Investment Law: With cross-border business expanding, legal experts in this field help organizations navigate treaties, trade policies, and dispute resolutions.
Salary & Scope in India
Law is one of the most rewarding professions when it comes to both career growth and financial stability.
After LLB: Fresh graduates usually start with packages ranging between ₹3–6 LPA in corporate law firms, legal consultancies, or as in-house counsels. Those who choose litigation may begin with a modest income, but as they build experience, reputation, and clientele, their earning potential increases significantly.
After LLM: With an advanced specialisation, graduates often step into higher-paying roles. In India, salaries for LLM graduates typically range from ₹6–12 LPA, depending on their expertise (e.g., corporate law, intellectual property, international law). Many are recruited into top law firms, think tanks, universities, and research organisations.
Law Courses at K.R. Mangalam University
K.R. Mangalam University offers a wide range of law courses designed to build strong legal knowledge, critical thinking, and practical skills. The programmes combine classroom learning with moot courts, internships, and industry exposure, preparing students to become confident legal professionals and justice-driven leaders.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
Undergraduate Programmes:
- B.A. LL.B. (Hons.): A 5-year integrated programme combining arts and law.
- BBA LL.B. (Hons.): A 5-year integrated programme combining business and law.
- LL.B. (Hons.): A 3-year programme for those who have already completed a bachelor’s degree.
Postgraduate Programme:
- LL.M.: A postgraduate programme offering specialisations including criminal law, corporate law, business law and ,more.
Conclusion
If you’re passionate about law and want to make a career in the field, LLB and LLM are two of the most important career path for you. LLM is the first step of legal education where students learn the fundamental understanding of the law. On the other side, the LLM offers an advanced sepecializarion legal education which enhances the expertise and open doors to higher-level positions.
Also Read: LLB after 12th: Eligibility, Career, Entrance Exams
FAQs
What is the full form of LLB and LLM?
The LLB stands for is Bachelor of laws and LLM stands for Legum Magister. Both the programmes are popular legal education course. The LLM stands for Legum Magister and pursued by those either holding an undergraduate academic law degree.
What is the duration of the LLB and LLM courses?
The duration of the LLB course in India is 3 Years and for integrated LLB its 5 years. Plus, LLM is a master programme after LLB and it’s of 2 years.
How is LLB different from LLM in terms of specialization?
As compared to LLB, the level of LLM is higher because it allows students to focus on specific fields like corporate governance, international law, human rights and intellectual property. Studying LLM after LLB is an important part that allows students to advance their legal careers or transition into niche legal fields.
What career opportunities are available after completing an LLM?
After complting the LLM course, there are several opportunities open for students. The LLM degree gives students a higher level of position in law firms. After completing the programme, students can pursue careers in advocates, district and session judge, notary, solicitor, court reporter, etc.



